Read every detail regarding the regulator of the Insurance Industry, IRDAI, which is responsible for the protection of all the interests of policyholders, efficient settlement of all genuine claims, and sustainable development of the insurance industry.
Overview:
You must have heard about IRDAI if you plan to buy an insurance policy or are already a policyholder with any insurance company in India. You, as a policyholder, are looking for the best fix for your issue regarding insurance claims, insurable interest, or related. When nothing works out the right way, the autonomous body IRDAI is responsible for aiding you with the most suitable solution with all the transparency and legitimacy in the system. Keep reading this article as you will get to know the full form of IRDAI and every significant detail and its functioning.

What is IRDAI?
The Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India is the full form of IRDAI or IRDA. It is a standalone and autonomous body that regulates every single aspect and operation of the insurance industry in India. IRDAI is liable to protect the interests of the policyholders having general insurance or life insurance, also responsible for developing the insurance industry in India.
History and Establishment of IRDAI:
The insurance industry in India has been ingrained since 1818, but by that time, the functioning was dominated by foreign companies. After an extended period, in 1973, the general insurance business was nationalized. By then, the Indian Insurance sector was protected. In 2000, IRDA was set up as a legal body under IRDA Act-1999 following the proposal of the Malhotra Committee. This allowed foreign companies to invest up to 26% in the Indian Insurance industry; later on, the limit was increased to 49%, which expanded the development of the insurance sector. Over the years, IRDA has protected the insurance industry from discriminatory practices and the policyholders' rights.
Objectives of IRDAI:
The insurance market in India is vast; hence, becomes an urgent need for a regulatory body that oversees all the operations and protects the people's interests. The key objectives of forming IRDAI are-
- To protect the interests of the policyholders.
- The constant growth of the insurance industry.
- Speedy settlement of genuine claims to exclude any insurance fraud.
- Ensure an effortless grievance redressal mechanism.
- Take adequate actions when necessary to protect the level of laws.
- Promote the fairness and transparency of laws to build the trust of policyholders.
Organizational Setup of IRDAI:
IRDAI is a ten-member body that is timely appointed and regulated by the Government of India. The head office of IRDA is in Hyderabad, ensuring insurers' financial development and stability. The key organizational setup of IRDAI is-
- One Chairman (For 5 years or maximum age of 60 years)
- Five whole-time members (For 5 years or maximum age of 62 years)
- Four part-time members (not more than 5 years)
All the members are supposed to work as a team, not individually, to perform any operation in the insurance industry. Mr Debasish Panda took charge as the current chairman (as of April 2023) of IRDAI influential from 13 March 2022, appointed by the Government.
How does IRDAI Work?
As the key statutory body in the insurance industry, IRDAI plays a significant role in ensuring that the rules and regulations are clear and in favour of the consumers buying the policies of any insurance company. IRDA is responsible for bringing necessary amendments to secure the interests of the policyholders. Also, provides the necessary solution in case of disputes.
Key Responsibilities of IRDAI:
Other than protecting policyholders' interests and maintaining the insurance industry's standards, other crucial functions of IRDAI are listed under Section 14 of the IRDA Act-1999. Let's go through the powers that IRDA Act allows to the authority-
- IRDAI holds the authority to issue registration certificates/licenses to the insurance companies and regularly takes care of the renewal, suspension, cancellation, modification, or re-issuance of the certificates/licenses per the rules and regulations.
- Protects the interests of the policyholders and related concerns like assigning the policy, nominations, settlement of claims, surrender value, and protecting the terms and conditions mentioned in the contract.
- Grants the registration certificates to new insurance companies to operate in India.
- Adheres to the requisite qualification and takes care of the necessary training of the insurance intermediaries and agents.
- Due to the numerous insurance companies present in the market, IRDAI clarifies the code of conduct of the surveyors and loss assessors.
- IRDAI regularly oversees the functioning of the insurance companies and conducts continuous audits to prevent any damage to the policyholder's rights.
- Adequately forms a management system that promotes the efficiency of the insurance business.
- Regularly enforces the necessary fees and regulates investment of funds by insurance companies.
- Continuously regulates and controls the rates, advantages, and terms & conditions the insurers offer.
- Trains the insurers and insurance intermediaries in maintaining the account books and records. Also, assesses how the final accounts should be maintained.
- IRDAI ensures that the claim of the policyholder is only allowed if the claim falls outside the coverage or contradicts the terms mentioned in the contract.
- IRDAI also supervises Tariff Advisory Committee under section 64U of the Insurance Act, 1938 (4) for their control and operations.
- Adjudication of any disputes that may arise between the insurer and intermediaries or insurer intermediaries.
- Specifies the percentage of standard premium income of the insurer to finance schemes.
- Regulates the fund investment of insurance companies and maintains their margin of solvency.
- Determines the percentage of life insurance business and general insurance business to be undertaken by the insurer that aids the equal development of both the rural and social sectors.
- Maintains the standard of the insurance industry so that people looking to buy a policy may find it reliable and trustworthy.
Benefits of IRDAI:
As every industry needs discipline and a code of conduct to function correctly without any damage to the system, for the same cause, there was an urgent need for the establishment of IRDAI to regulate the finance and insurance industry. The primary benefit of the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority is that it strictly maintains the efficient operation of the overall insurance market, ensuring that the rights and interests of the policyholders are protected. Hence, IRDAI ensures fair practices for the sustainable development of the insurer and policyholder.
Types of Insurance Regulated by IRDAI:
The insurance sector is broadly categorized into two sections, first, Life Insurance and second, Non-life insurance, also known as General Insurance. The following are the successive types of the two categories-
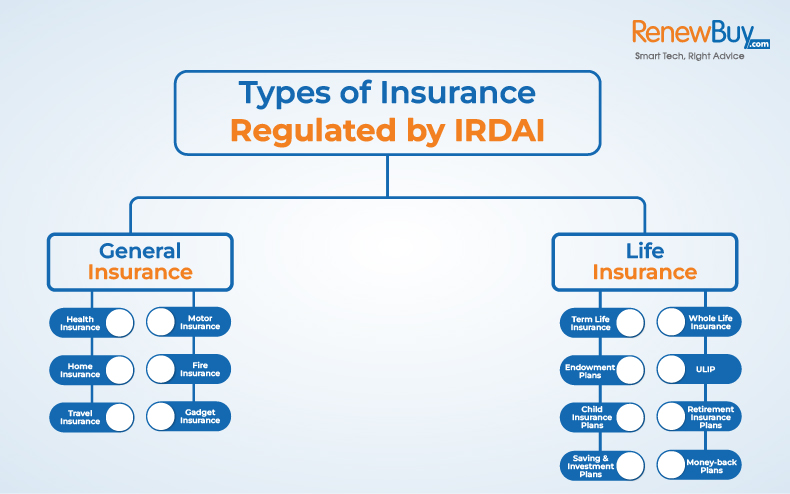
General Insurance:
IRDAI has listed around 34 non-life insurance companies in India. The following are the types of non-life insurance or general insurance plans offered by the companies-
- Health Insurance
- Motor Insurance
- Home Insurance
- Fire Insurance
- Travel Insurance
- Gadget insurance
Life Insurance:
Around 24 life insurance companies are listed under IRDAI, which offers various types of life insurance policies to consumers. We have listed the most common types of life insurance plans available in India:
- Term Life Insurance
- Whole Life Insurance
- Endowment Plans
- Unit-Linked Insurance Plans
- Child Insurance Plans
- Retirement Insurance Plans
- Saving & Investment Plans
- Money-back Plans
Allowance of Electronic Format of Insurance Policies by IRDAI:
The IRDAI encourages the electronic format of your insurance policies to make the system more flexible and operations transparent. If you want to convert your insurance policies into electronic format, you will be delighted that IRDAI has allowed electronic conversion to reduce the hassle. All existing life insurance, general insurance, health insurance, and annuity policies can be converted into digital format. You need to raise a request to the insurance company registered under IRDAI or the insurance repository to allow the necessary changes.
What are the Unique Rights of IRDAI?
As mentioned in section 14 of the IRDA Act 1999, the authority plays a vital role in the insurance industry's regulations, management, development, and promotion. Let's have a glance at the unique rights of IRDAI-
- Forming and simplifying all the codes of conduct and rule and regulations in the insurance industry.
- Assessing the ongoing operations of an insurance company.
- To levy reasonable charges to perform the purpose of the act.
- Regulate the maintenance of margin solvency.
- Ensure that accurate information has been passed on about the products and services.
- Takes care that the Government is doing everything to ensure uniformity and accountability in the insurance sector.
- Furnish all the documents, returns, statements, and other government demands.
- In case of any disputes between the insurer and intermediaries, IRDAI can step in as an adjudicator.
- Control and regulate the terms and rates where TAI cannot interfere.
- Has the power to control the other professional organizations that are involved in the business of insurance and reinsurance. Also, IRDAI decides the percentage of income that the organizations will receive from the insurance companies.
Grievance Redressal Mechanism of IRDAI:
Consumer satisfaction is essential for any industry to grow. The insurance industry also offers a facility where consumers can connect and express their experiences or file a complaint to gain a suitable solution. A grievance is a vital communication that expresses the consumer's or policyholder's dissatisfaction regarding any policy or towards the insurance company when they find a lack of action of a specific law or feel cheated. The efficient grievance redressal mechanism of IRDAI ensures that the consumers are dealt with fairly by all means with an open mind and transparency.
The consumer reaches the insurance company to express dissatisfaction; if not heard, this can further reach the consumer forum. The following is the Grievance Redressal Mechanism of IRDAI for the expression of discontent-
Step 1: Reaching the Insurance Company:
The first step is to reach the insurance company as the IRDA mandates their grievance cell. The contact details must be listed in the policy document or brochure. You can directly make a call, write a mail or letter to the address given. If in case, you are still waiting for a response to your complaint within 15 days; you can reach out to the company's regional or central office to state that your concern still needs to be addressed. Now, you need to wait for 30 days after filing the complaint. If you still do not get a positive response, you can raise your concern to IRDAI.
Step 2: Approaching IRDA:
To protect the rights of the policyholders, the IRDA has formulated a grievance redressal mechanism. You can directly approach IRDAI via the alternative channel "Bima Shikayat- IRDAI Grievance Call Centre" to lodge complaints and track the status of the same. Another portal called "Bima Bharosa- Integrated Grievance Management System (IGMS)' is formed where prospects can file complaints per pre-defined rules. You can reach out to IGMS through www.igms.irdai.in and register your complaint. After your complaint, IRDA follows up with the concerned insurance company to check the status. If you do not get a solution, we recommend you go for an insurance ombudsman.
Step 3: Filing to an Insurance Ombudsman:
You must be wondering what an insurance ombudsman is. An insurance ombudsman is a non-judicial arbitrator appointed by the Government of India for the individual policyholder to settle their complaints in a court system most cost-effectively and efficiently. A person themself, their legal heirs, or nominees can file a complaint to an insurance ombudsman of their territory regarding their grievance against any insurer. The policyholder can reach the insurance ombudsman within 12 months of the dispute in the following conditions:
He/she has first reached the insurance company with the complaint and-
- They have rejected the dispute raised.
- Not resolved it to your satisfaction or have yet to acknowledge within 30 days.
- The claim's value, including all expenses, is at most 30 lakhs.
The insurance ombudsman will work as a mediator and arrive at a fair solution based on the facts. If you are satisfied with the settlement, the ombudsman will inform the insurance company to comply with the terms within 15 days. If the settlement doesn't work for the complainant, the ombudsman will pass an award within 3 months after receiving all requirements and will be binding upon the insurance company. Once the award is passed, the insurer needs to comply with the award passed within 30 days. The decision of the insurance ombudsman is final and binding.
Step 4: Consumer Forum:
When you are not satisfied with the settlement of the insurance ombudsman, the consumer forum is your next stop to settle your grievance. A consumer forum is a district court where you prepare for the hearing of your case with the help of a lawyer. There's no need to pay any additional charges or fees to the forum for filing your complaint. You can reach a consumer forum only within 2 years of your grievance filing date. The claim amount decides the correct consumer forum for the hearing of your case. If your claim amount is up to 20 lakhs, the forum at a district level will help you; if the claim amount is above 20 lakhs and up to 1 crore, the forum at a state level will help you. If the claim amount is above 1 core, then the National Forum will play the part.
How Does IRDAI Benefit the Insurers?
As a regulator of the insurance industry, IRDA oversees all the activities for the sustainable development of insurers. IRDA works to bring all the Indian and foreign insurers in the same tune to make the insurance market competitive enough. Also, IRDA plays a vital role in insurers excluding any monopoly in the market while focusing on a higher level of integrity and transparency in the system.
How Does IRDAI Benefit the Customers?
In 2002, the IRDA passed a resolution called IRDA (Protection of Policyholder's Interests). By then, the IRDA is responsible for making every single effort and monitoring all the terms, operations, and functioning of the insurance industry, insurers, agents, and intermediaries. The sole purpose of IRDA is to ensure that the interests of the policyholders are safeguarded from the very first start of buying the policy to the time of settlement of the claims. If the policyholders are not satisfied with the settlement at the company level, they can directly reach IRDA with the help of a grievance redress mechanism.
New Rules and Guidelines by IRDAI for Health and Mediclaim Insurance:
After the outbreak of Covid-19, every individual is aware of having health insurance for themself and their family. With time, healthcare costs are rising rapidly; hence, health insurance is becoming necessary for everyone to get quality care. For the betterment of insurers and policyholders, IRDAI launched some new rules and guidelines for health and medical insurance in 2020. This set of rules is enforced from 1 April 2021. You can have a look at these updated IRDA guidelines below-
Rejection of Claims:
If the policyholder has continuously renewed the policy for at least 8 years without any break or lapse, the insurer cannot reject the health insurance claim. These 8 years will be considered the moratorium period. The insurer cannot reach out to IRDAI for rejection of the claim except in the case of fraud or malfunctioning or the claim falls under the exclusion of a health insurance policy.
Telemedicine Inclusion:
With the rise of digitization, the IRDAI has allowed policyholders to seek online consultations from qualified doctors without worrying about high consultation fees. To protect the interests of the policyholders, insurers are forced to introduce "Telemedicine Consultation" to their health insurance policies.
Claim Settlement:
The insurer must settle the claim amount within 30 to 45 days after the policyholder submits the necessary documents. If it fails to do so, the insurer will pay the interest on the amount of the claim.
Check the best life insurance companies that "RenewBuy" has picked for you.
Bottom Line:
We are sure that by now you know what IRDAI is and what are the decisive roles of IRDAI in the insurance industry. With the everchanging requirements, it becomes vital to implement the terms that fulfil the expectations of both the insurers and policyholders. To keep the pace of quality and sustainable growth of the insurance industry in line, IRDAI encourages new insurers in the market. By eliminating frauds and mishappening in the insurance market, the IRDAI plays a vital role in strengthening the economy of the Nation.
